Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 289-298
核磁共振成像(MRI)是一种非侵入性成像技术,可产生具有高软组织对比度和空间分辨率的三维详细解剖图像。目前,MRI造影剂已成为诊断某些疾病的MRI程序不可缺少的一部分,因为在许多情况下添加MRI造影剂可以提高敏感性和特异性,从而可以更好地区分病理组织。MRI的造影剂主要有顺磁性Gd化合物和超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒(SPIO)两种类型。顺磁性Gd化合物会影响水质子的自旋-晶格(T1)对比度,而SPIO会缩短水分子的自旋-自旋弛豫时间(T2),并用于T2成像。然而,单一的MR对比过程有一些固有的缺点,例如:(1)在T2成像中,钙化、出血或金属沉积引起的干扰,以及(2)疾病组织的信号强度不足以在T1成像中。这些缺点使得正常组织和疾病组织难以区分,并且可能严重限制对诊断图像的准确解释。因此,开发利用单扫描仪设备的多功能成像模式以获得更准确的诊断信息是必要的。
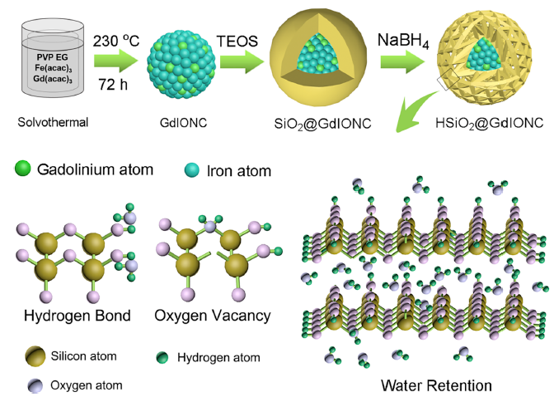
近日,上海交通大学邹多宏教授和温州医科大学徐云升教授报道了一种通过改变纳米结构和增加水的相互作用来制备高性能双模核磁共振显影剂的有效策略。HSiO2@GdIONC具有嵌套的介孔核壳结构,可通过物理吸附和氢键、氧空位相互作用有效地结合大量水分子,从而显著提高T1和T2的对比能力。此外,与纯GdIONC(10.5)相比,HSiO2@GdIONC的r2/r1比值降低至8.3,有效防止了T1和T2成像的相互干扰,使HSiO2@GdIONC表现出最佳的双模对比能力。细胞和动物实验结果进一步表明,HSiO2@GdIONC在肝脏区域显示的T1和T2加权MR对比要好于纯GdIONC。
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that produces three dimensional detailed anatomical images with high soft tissue contrast and spatial resolution. By now MRI contrast agents have become an indispensable part of MRI procedure for the diagnostics of some diseases, since their addition in many cases improves sensitivity and specificity and therefore provide better distinction of pathological tissues. There are two main types of MRI contrast agents, paramagnetic Gd compounds and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIOs). Paramagnetic Gd compounds affect the spin-lattice (T1) contrast of water protons, whereas SPIOs shorten the spin-spin relaxation time (T2) of water molecules and are used for T2 imaging. However, a single MR contrast process has some inherent drawbacks, for example: (1) disturbances originating from calcification, bleeding, or metal deposits in T2 imaging and (2) insufficient signal intensity in disease tissue for T1 imaging. These drawbacks are difficulty in discrimination between normal tissue and disease tissue and may seriously limit accurate interpretation for the diagnosis image. Therefore, developing multifunctional imaging modes using a one-scanner device to obtain more accurate diagnosis information is necessary.
Recently, Professor Zou Duohong from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School and Professor Xu Yunsheng from Wenzhou Medical University reported an efficient strategy to prepare a highperformance dual-mode MRI contrast agent via modifying the nanostructure and increasing the number of water interactions. HSiO2@GdIONC has a nested, mesoporous core structure and can effectively bind abundant water molecules via physical absorption and hydrogen-bond and oxygen-vacancy interactions, dramatically improving the T1 and T2 contrast ability. In addition, compared with that of bare GdIONC (10.5), the r2/r1 ratio of HSiO2@GdIONC decreased to 8.3, effectively preventing the disturbance of T1 and T2 imaging and allowing HSiO2@GdIONC to exhibit an optimal dual-mode contrast ability. Based on the results of the cell and animal experiments, HSiO2@GdIONC showed better T1- and T2-weighted MR contrast in the liver region than bare GdIONC.
doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.219
(郝莉莉)