蚕丝蛋白/纳米碳链复合支架体内及体外骨再生
Biomaterials 136 (2017) 67 – 85
| 近年来纳米复合材料由于可结合个体特性而在在组织修复中的潜在应用逐渐被重视。印度理工大学生物研究中心在本研究对骨修复的微环境进行的深刻的研究。理想的骨修复材料应为一种可降解的免疫性较低的骨支架且其力学性能应与人体骨骼相识。
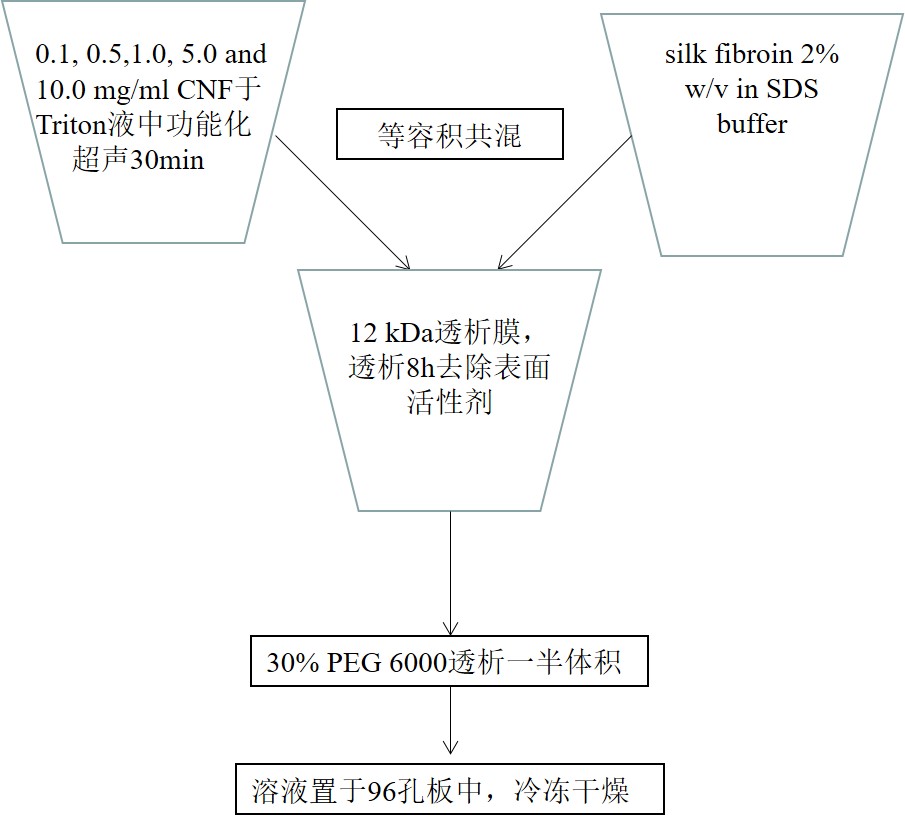
蚕丝蛋白为一种天然可降解且生物相适行较好的骨修复材料,其对骨基质的分泌具有促进作用。其自身存在的连接肽链-Arg-Gly-Asp- 对于细胞具有粘附作用。纳米碳纤维共混于蚕丝蛋白中可加强支架的力学性能,且纳米碳纤维的电传导性对于细胞的生长具有促进作用。于3D复合支架中担载BMP-2及TGF-β1增强材料的潜在的骨修复能力。结果表明:由于这些复合基质材料的作为一种细胞外基质对于骨修复具有较大的促进作用。 In recent years the potential application of nanocomposite biomaterials in tissue engineering field is gaining importance because of the combined features of all the individual components.Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur made a bottom-up approach is acquired in this study to recreate the bone microenvironment .The major rationale behind bone tissue engineering is the need for reconstruction of biodegradable bioactive non-immunogenic orthopedic implants with better filler material and mechanical strength close to the biological anatomy. Non-mulberry tropical tasar Antheraea mylitta is considered as an important natural polymer amongst several synthetic polymers for supporting as an extracellular matrix (ECM) for bone. The inherent integrin binding tripeptide -Arg-Gly-Asp- motif [UniProtKB _ Q81SB3: fiveRGD motifs present in the partial CDS of 507 amino acids] aids firm cellular adhesion. Carbon nanofiber are already known for their pronounced electrical, mechanical,thermal, and structural properties. dual growth factor (BMP-2 and TGF-b1) loaded three dimensional CNF reinforced nonmulberry silk protein fibroin nanocomposite sponges and investigating their potential as bone tissue construct for the first time. The study clearly shows the potential attributes of these composite matrices as an extra cellular matrix for supporting successful osseointegration process. (万腾) |