|
四种磷酸钙陶瓷诱导小鼠异位骨的形成过程
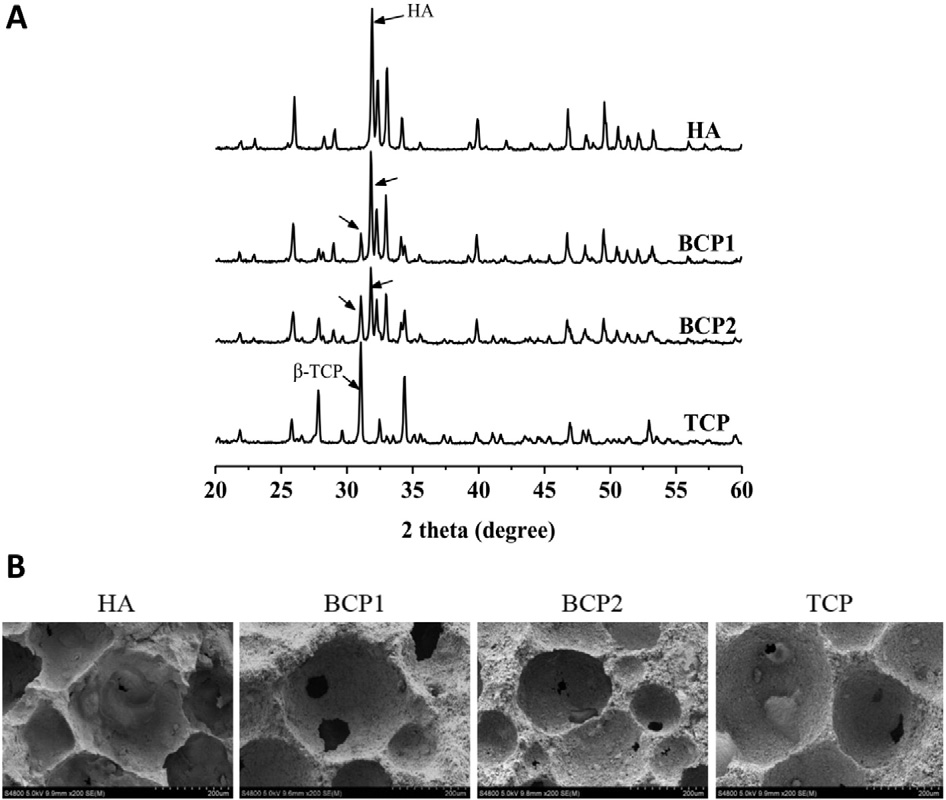
Materials Science and Engineering C 70 (2017) 1000–1010 临床上对于大块骨缺损的修补与治疗广泛热议。移植物的选择主要有三类,包括自体骨、同种异体骨及合成材料,各有优劣,存在争议。其中CaPcs可以模拟自体骨的强度,并被证明具有良好的生物相容性、骨传导性、骨诱导性。尤其是骨诱导性被广泛关注,体外细胞实验已经在信号通路和蛋白表达方面验证想法,目前尚缺少权威的体内试验。 最近,四川大学张兴栋院士团队根据体外试验结果设计了一个完整的体内试验。首先,合成并表征了四种磷酸钙材料。然后他们对老鼠进行活体实验建模。在4周和16周观察到组织学和显微变化。最后定量分析了PCR和IHC筛选的几种成骨mRNA和蛋白。他们的结论是,从基因、蛋白质和组织水平可以证明CaPcs具有骨诱导活性。此外,骨诱导的强弱与相组成密切相关。 Recently, the repair and treatment of large bone defect has been widely discussed in clinic research. There were three main types of graft options, including autogenous bone, allogeneic bone, and synthetic materials.They all had their pros and cons. The CaPcs could simulate the strength of the autologous bone and was proved to have good biocompatibility, osteoconductivity and osteoinductivity. In particular, its osteoinductivity has been widely concerned. Vitro cell experiments have proved the idea of signaling pathways and protein expression, however, there is still a lack of authoritative vivo experiments. Recently, the author’s team designed a complete vivo test based on its vitro test results. First, four kinds of calcium phosphate materials were synthesized and characterized. They then modeled the mice for vivo experiments. Histological and microscopic changes were observed at 4 and 16 weeks. Finally, they quantitatively analyzed several osteogenic mRNA and proteins screened by PCR and IHC. They concluded that CaPcs could be proved to have osteoinductivity from gene, protein and tissue levels. In addition, the strength and weakness of bone induction were closely related to the phase composition. (马一行)
|
|---|