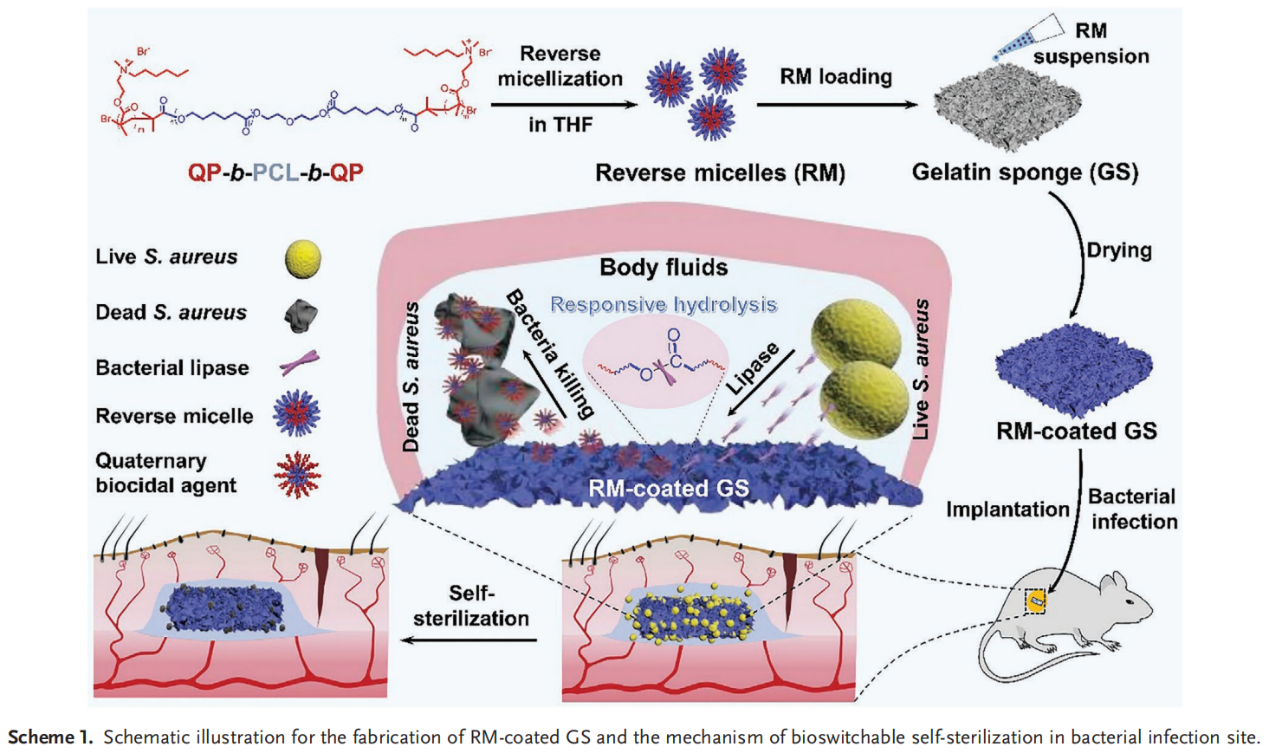
获得性细菌感染对公众健康构成威胁。因此,对具有本体杀菌植入式敷料的开发需求越来越大。该文合成了一系列季铵化三嵌段共聚物,即QP-b-PCL-b-QPs,并在四氢呋喃中自组装成反胶束(RMs)。RMs在壳中含有生物相容性聚己内酯(PCL)块以提供生物安全性和响应性,在核心中含有生物杀灭剂四元块以提供抗菌活性。在有细菌脂肪酶存在的情况下,可生物降解的PCL段落被水解,导致四元生物杀灭剂(QBAs)的响应性释放以实现自我灭菌。RMs可以方便地浸渍到明胶海绵(GS)中制备RM2包被的GS,在脂肪酶存在下具有很强的抗菌活性。与革兰氏阴性菌相比铜绿假单胞菌,革兰氏阳性菌,金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草杆菌对RM2包衣GS释放的QBAs更敏感。体内抗菌实验和组织学分析进一步证实了RM2包被GS在减少小鼠细菌感染方面的有效性。这些结果共同为开发可生物开关的自杀菌敷料以减少医疗保健获得性细菌感染提供了一个有希望的策略。
Healthcare-acquired bacterial infections are a threat to public health. Therefore, development of self-sterilizing implantable dressing materials is in increasing demand. Herein, a series of quaternized triblock copolymers, namely, QP-b-PCL-b-QPs, are synthesized and self-assembled into reverse micelles (RMs) in tetrahydrofuran. The RMs contain biocompatible poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) blocks in the shell to render biosafety and responsiveness, and biocidal quaternary blocks in the core to render antibacterial activity. In the presence of bacterial lipase, the biodegradable PCL blocks are hydrolyzed, resulting in the responsive release of quaternary biocidal agents (QBAs) to enable self-sterilization. The RMs can be facilely impregnated into commercial gelatin sponge (GS) to fabricate RM2-coated GS, which impose potent antibacterial activity in the presence of lipase. Compared to Gram-negative P. aeruginosa, the Gram-positive S. aureus and B. subtilis are more susceptible to QBAs released from RM2-coated GS. The in vivo antibacterial assays and histological analyses further confirm the validity of RM2-coated GS in reducing bacterial infection in mice model. These results, taken together, provide a promising strategy for the development of bioswitchable self-sterilizing dressing materials to reduce healthcare-acquired bacterial infections.
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202011165
李建超