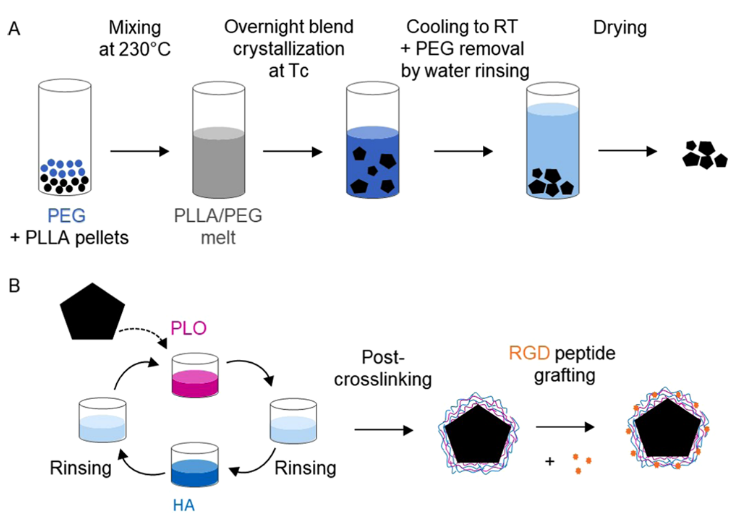
微载体上的细胞培养作为二维培养的替代产生大剂量的细胞,这是基于细胞的治疗所需要的。在此,比利时天主教鲁汶大学Karine Glinel教授报告了一种基于生物源和可降解聚合物的多功能、易操作的无溶剂绿色制造工艺,用于制备微载体。微载体核心的制备是基于聚合物混合物的聚(L-丙交酯)结晶,使我们能够轻松调整密度、孔隙率和微粒的大小。基于生物聚合物的生物粘合剂涂层,不含动物蛋白,优化以提高细胞粘附性,然后成功地沉积在微载体的表面。这些新的微载体能够在半静态和动态条件下,以良好的产量扩展人类脂肪来源的基质细胞。最后,珠-珠细胞转移被证明可以在不停止培养的情况下提高细胞产量。因此,这些微载体是目前现有系统的一个有前途和高效的绿色替代品。
Cell culture on microcarriers emerges as an alternative of two-dimensional culture to produce large cell doses, which are required for cell-based therapies. Herein, we report a versatile and easy solvent-free greener fabrication process to prepare microcarriers based on a biosourced and compostable polymer. The preparation of the microcarrier core, which is based on poly(L-lactide) crystallization from a polymer blend, allows us to easily tune the density, porosity, and size of the microparticles. A bioadhesive coating based on biopolymers, devoid of animal protein and optimized to improve cell adhesion, is then successfully deposited on the surface of the microcarriers. The ability of these new microcarriers to expand human adipose-derived stromal cells with good yield, in semistatic and dynamic conditions, is demonstrated. Finally, bead-to-bead cell transfer is shown to increase the yield of cell production without having to stop the culture. These microcarriers are therefore a promising and efficient green alternative to currently existing systems.
DOI:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.0c16875
周小松