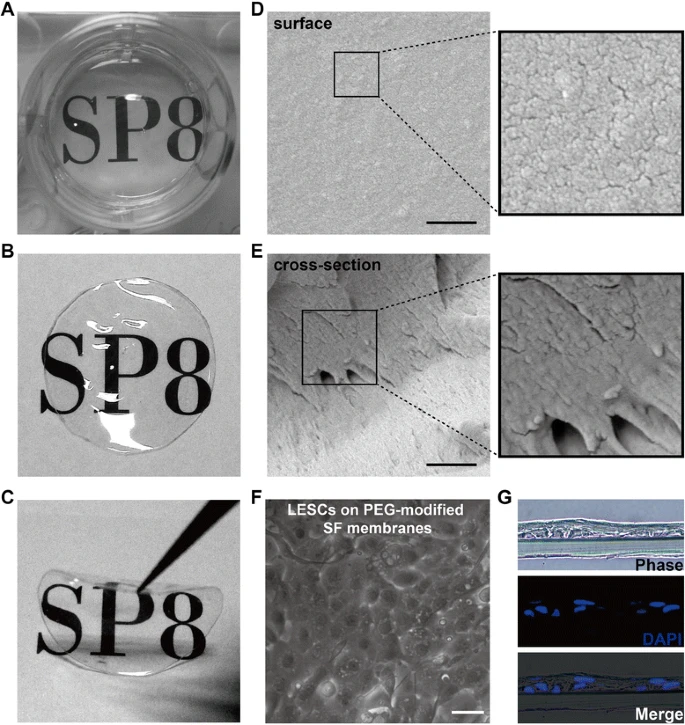
角膜上皮由五到六层细胞组成。完整的角膜上皮层在维持眼表面稳定性和光学透明性方面起着重要作用。鳞状上皮作为抵御外部环境的第一道保护屏障,不断更新。角膜缘中的角膜缘上皮干细胞是角膜缘上皮干细胞的生态位,在角膜上皮的稳态和再生中起着重要作用。化学(碱/酸)或热损伤、紫外线和其他电离辐射以及细菌和病毒感染等因素会损伤角膜上皮细胞,包括角膜缘区域的细胞。在严重损伤的角膜中,角膜缘和中央角膜上皮都不存在,导致结膜上皮细胞侵入角膜表面。结膜化、新生血管化、上皮下疤痕和睑球粘连的形成严重影响角膜的透明度,甚至导致视力障碍。这些疾病被称为角膜缘干细胞缺乏症(LSCD)。角膜缘上皮干细胞在角膜上皮稳态和再生中起重要作用,对角膜缘的损伤将导致LSCD,并伴有结膜化甚至视力障碍。培养的胚胎干细胞已被用于眼表重建,丝素膜已显示出作为LESC培养基质的潜力。培养方法和胚胎干细胞的携带者都会影响LESC移植后的结果。丝素蛋白是一种很有前途的生物材料,因为它具有广泛的可获得性、相对较低的成本和成熟的生物相容性。在眼组织重建中,丝素膜比其他天然和合成生物材料具有潜在的优势。结果提示组织外植体和单细胞悬液培养的角膜上皮细胞更适用于眼表重建。LESC/丝素移植修复角膜上皮缺损并逆转LSCD,聚乙二醇修饰的丝素膜适合作为LESC移植的载体。
The corneal epithelium consists of several stratified layers that are five or six cells thick. A complete corneal epithelial layer plays an important role in maintaining ocular surface stability and optical transparency. As the first protective barrier against the external environment, squamous epithelia are constantly renewed. Limbal epithelial stem cells (LESCs) in the limbus, the niche for LESCs, play important roles in corneal epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Several factors such as chemical (alkali/acid) or thermal injuries, ultraviolet and other ionizing radiation, and bacterial and viral infections can damage the corneal epithelial cells, including those of the limbal areas [5, 6]. In a severely injured cornea, the limbal and central corneal epithelia are both absent, resulting in conjunctival epithelial cells invading the corneal surface. The conjunctivalization, neovascularization, subepithelial scarring, and symblepharon formation severely affect the corneal transparency and even lead to visual impairment . These diseases are called limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD). Limbal epithelial stem cells (LESCs) play important roles in corneal epithelial homeostasis and regeneration, and damage to the limbus will lead to limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD), with conjunctivalization and even visual impairment. Cultured LESCs have been used for ocular surface reconstruction, and silk fibroin (SF) membranes have shown potential as a substrate for LESC cultivation. Both culture methods and the carriers of LESCs affect outcomes following LESC transplantation. SF is a promising biomaterial owing to a variety of factors including its wide availability, relatively low cost, and proven biocompatibility. In ocular tissue reconstruction, SF membranes possess potential advantage over some other natural and synthetic biomaterial.
DOI:10.1186/s13287-017-0707-y.
王丽