J Mater Chem B 2020 07 07
生物质水凝胶已广泛应用于生命科学,值得注意的好处包括它们的降解性、绿色来源和生物相容性。透明质酸是一种广泛存在于细胞外基质中的众所周知的生物材料。它是一种无免疫原性、可降解和高度生物相容性的天然聚合物,在多种生物过程中发挥重要作用。此外,透明质酸具有优异的保水性,由其制备的水凝胶具有含水量高、透明性好、生物相容性好等优点。然而,它们的机械强度随着含水量的增加而降低。此外,这些水凝胶的高精度成型具有挑战性,这极大地限制了它们的应用。
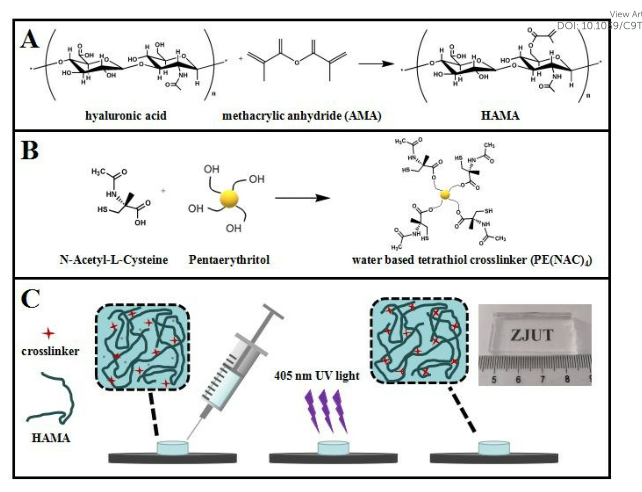
以大幅度改善生物医用材料与生物体的相容性为目标,北京市生物医学工程高精尖创新中心常凌乾教授与浙江工业大学陈枫副教授、浙江大学附属第二医院刘震杰副主任医师合作,结合紫外光引发和巯基“click”聚合两种方法,使用光影印法制备了一系列力学性能优异、无毒无污染、生物可降解的微米级表面图案化高分子材料。合作团队选择高分子量透明质酸前体,分子链经过双键改性,与水溶性四半胱氨酸交联剂复配成水溶液,在波长405纳米紫外光辐照下,快速固化为无毒无小分子污染、体内可降解的透明质酸水凝胶,其含水量可达95 wt%以上。
Biomass hydrogels have been widely used in the life sciences. Notable benefits include their degradability, green origin and biocompatibility. Hyaluronic acid is a well-known biomaterial that is widely present in the extracellular matrix (ECM). It is a non-immunogenic, biodegradable and highly biocompatible natural polymer that plays an important role in a variety of biological processes. In addition, hyaluronic acid has excellent water retention, and the hydrogels prepared from it have the advantages of high water content, good transparency, good biocompatibility and so on. However, their mechanical strength decreases with increasing water content. In addition, the high precision molding of these hydrogels is challenging, which greatly limits their application.
To greatly improve the compatibility of biomedical materials with organisms, Professor Chang Linggan of Beijing Advanced Innovation Center of Biomedical Engineering, Associate Professor Chen Feng of Zhejiang University of Technology and Deputy Chief Physician Liu Zhenjie of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University collaborated with Professor Chang Linggan of the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center of Biomedical Engineering to combine the two methods of UV triggering and mercapto “click” polymerization. A series of micron-scale surface patterned polymer materials with excellent mechanical properties, non-toxic, non-polluting and biodegradable were prepared by photocopying method. The high molecular weight hyaluronic acid precursor was selected by the team, and the molecular chain was modified by double bond, then mixed with the water-soluble tetracysteine crosslinking agent to form an aqueous solution. Under the irradiation of 405 nm ultraviolet light, the hyaluronic acid hydrogel was rapidly cured into a non-toxic and biodegradable hyaluronic acid hydrogel with a water content of over 95 wt% and no small molecule pollution.
DOI: 10.1039/C9TB02796C
赵岚岚