Biomaterials.264(2021)120446
虽然具有抗菌性的植入物其抗菌性能良好,包括经AMP改性的植入物,但其细胞毒性也不可忽视。其表面富含的抗菌基团降低了植入物的生物相容性、血管生成活性和成骨活性,进而延迟了骨重建且会增加体内感染的可能性。为了平衡抗菌活性和骨重建活性,非常需要可以调节生物活性的多功能抗微生物植入物。而现在的大多数植入物需要外部刺激:如光、电、温度等,但在体内这些较难实现,故静态通用的多功能抗微生物植入物更符合实际需求。混合肽(FP)近年来引起很多关注,它可以解决肽有限的结合位点以及不可控的空间和方向等问题。研究发现FP可以通过占据更少的反应位点而增加接枝肽的密度。因此它对于制备静态通用多功能抗微生物植入物具有很大的优势。但目前临床上还没有这种满足抗生物活性和骨重建活性期望的FP报道。
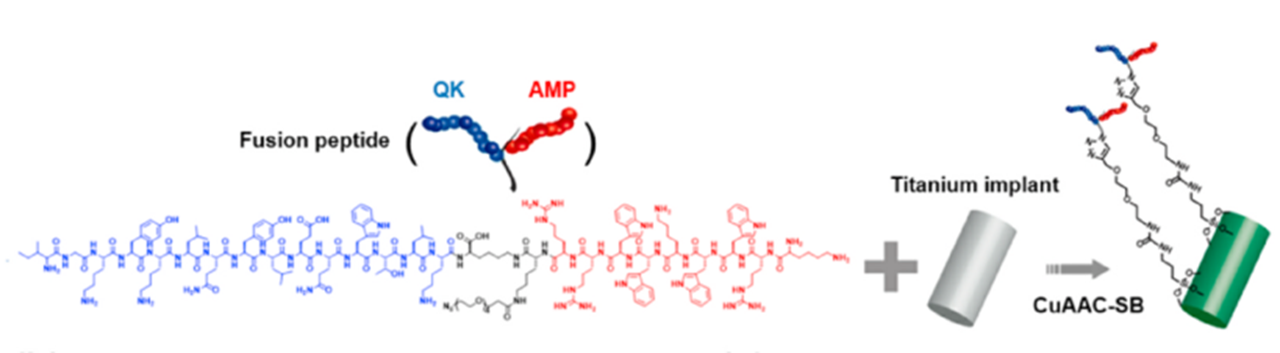
考虑到骨重建活性,VEGF(血管内皮生长因子)模拟肽是制备FP的候选。VEGF可以促进血管生成,同时具有促进骨改建的功能。但是VEGF具有高免疫原性和低稳定性,很多血管内皮生长因子的模拟肽被开发出来,如QK。它可以与VEGF受体结合,诱导血管生成,但它像VEGF一样的成骨活性尚未被证明。本研究通过在种植体表面设计一个具有HHC-36和QK序列的FP,来制备静态通用多功能抗微生物植入物。
近日,华南理工大学的王迎军教授报道了一种具有抗菌、成骨和成血管三种活性的静态通用植入物涂层的制备,该涂层能够增加植入物的抗菌性能,降低术后感染的发生率;且有良好的成血管和成骨性能,加快了植入物的骨整合效率,对于临床上减少生物材料感染的发生具有重要意义。
Despite their efficient antimicrobial activity, the cytotoxicity of antimicrobial implants, including AMP-based implants, remains a concern. The enriched antimicrobial agents on the surface reduced the biocompatibility, angiogenic activity and osteogenic activity of the implant, further delayed sufficient osseointegration and increased the risk of in vivo infection. To balance the antimicrobial and osseointegration associated activities, versatile antimicrobial implants with easily adjustable bioactivities are highly desirable. However, most of the current implants require external stimuli, including electricity, light and temperature, which are difficult to be conducted in vivo. Therefore, the “statically-versatile” implant with nonessential external stimuli would greatly facilitate the in vivo applications. In recent years, fusion peptides (FPs) with different bioactive se-quences have attracted much attention as they can exhibit versatile biological behaviors simultaneously, which can efficiently tackle the challenge of simple immobilization of the peptide mixtures with limited immobilization sites and uncontrollable space or orientation of peptides. Particularly, the FP on the implant surface can equivalently increase the grafting density of the specific peptides by occupying less reaction sites, demonstrating that FPs would be greatly advantageous for the development of a statically-versatile implant. However, to the best of our knowledge, the desired FP-engineered titanium implant that can fulfill the clinical requirements of antimicrobial activity and all of the abovementioned osseointegration-associated activities (biocompatibility, angiogenic activity and osteogenic activity) has never been reported.
Considering the osseointegration-associated activities, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mimetic peptides become potential candidates for the sequence of FP. VEGF is an important growth factor in modulating angiogenesis. It can greatly improve the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells and promote vascularization. As the high immunogenicity and low stability of VEGF, many VEGF-mimetic peptides were developed, such as QK with 15 amino acids to mimic the helix region 17–25 of VEGF. It can bind VEGF receptor, and further induce the improvement of angiogenesis. But it has been seldom proved that QK has osteogenic activity as VEGF. In the present study, we developed a “statically-versatile” titanium implant through immobilizing a designed FP containing HHC36 (AMP) sequence and QK sequence on implant surface.
Recently, Professor Wang Yingjun from South China University of Technology reported the preparation of a “statically-versatile” titanium implant, which is coating with fusion peptides(FPs), it has antibacterial, osteogenic and angiogenic activities. The coating can increase the antibacterial properties of the implant and reduce postoperative infections。Also, it has good angiogenesis and osteogenic properties, which can speed up the osseointegration efficiency of implants, and is of great significance for clinically to reduce the incidence of biological material infections.
DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120446
谢宁